Department
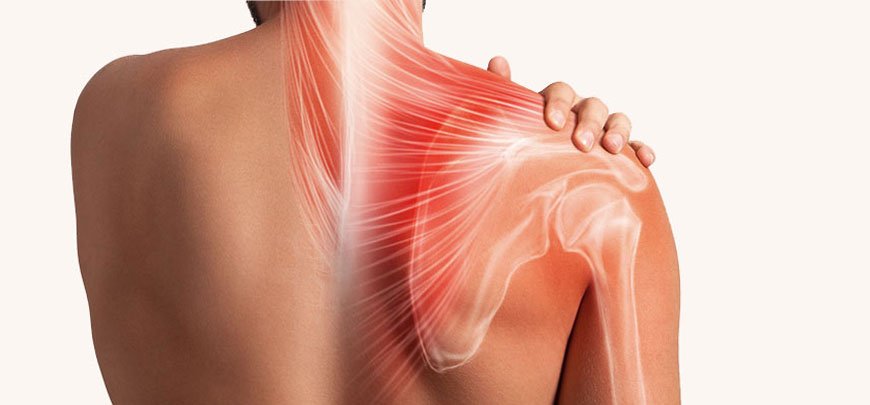
Shoulder Pain
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that worsen shoulder pain and reducing repetitive motions can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and numb pain, while heat therapy can improve blood flow and relax tight muscles.
Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, prescription medications or steroid injections may be recommended for more severe pain or inflammation.
Physical Therapy: A tailored exercise program designed by a physical therapist can help improve shoulder strength, flexibility, and range of motion. This may include stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, and manual therapy techniques.
Modalities: Modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or therapeutic massage may be used to help relieve pain and promote healing.
Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids directly into the shoulder joint can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation, especially for conditions like bursitis or tendonitis.
Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, or for severe injuries such as rotator cuff tears or shoulder instability, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or reconstruct damaged tissues.
he treatment approach for an ACL injury is individualized based on the patient’s specific circumstances and goals, with the aim of restoring knee function, stability, and returning to an active lifestyle.
