Department
Lumbar Spondylitis
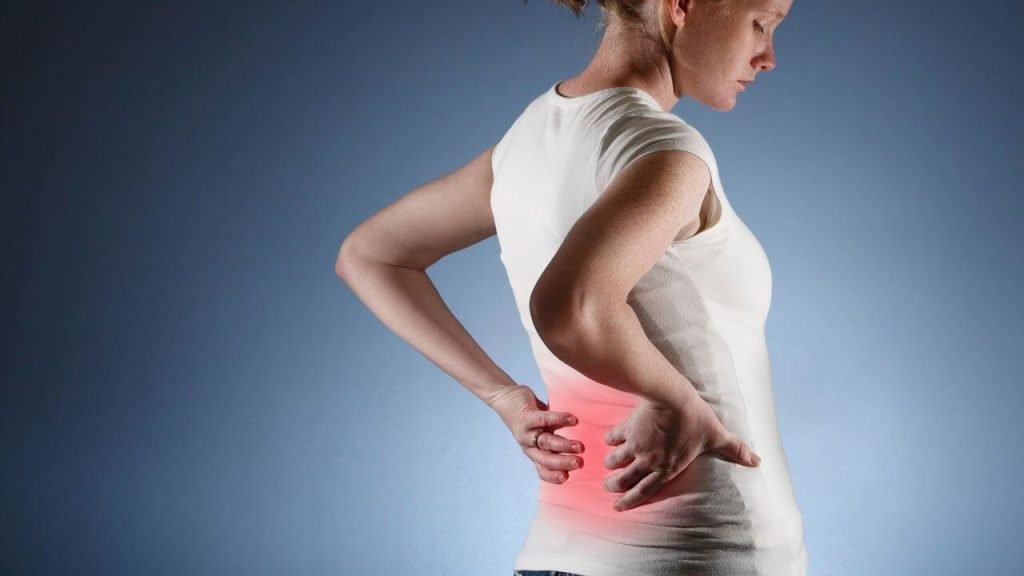
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and analgesics are commonly prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation associated with lumbar spondylitis. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the affected area to provide temporary relief.
Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and correct posture. Therapeutic exercises and techniques such as stretching, strengthening, and low-impact aerobic exercises can alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, adopting proper body mechanics, and incorporating ergonomic adjustments in daily activities can help reduce strain on the lumbar spine and alleviate symptoms.
Heat/Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Heat therapy may help relax tight muscles, while cold therapy can numb the area and reduce swelling.
Surgical Intervention: In severe cases of lumbar spondylitis where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or there is significant nerve compression, surgical interventions such as discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion may be considered to stabilize the spine and alleviate pressure on the nerves.
